Abstract
Introduction: Patients with RR-AML, particularly older adults, have dismal outcomes and limited therapy options. Given their tolerability, many RR-AML patients are treated with hypomethylating agents (HMAs). However, little data are available on how to best select patients with RR-AML for HMA therapy. The MRC and LRF developed the MRC/LRF score to predict which AML patients benefit from azacitidine as frontline therapy, but not in the refractory and relapsed setting. Using a large, international, multi-center database, we analyzed the performance of the MRC/LRF tool in the prediction of overall survival (OS) in RR-AML patients after therapy with HMAs.
Methods: Our database included retrospectively collected data from 655 patients with RR-AML who were treated with HMAs in the 2006 to 2016 period from 7 centers in the United States and 4 centers in Europe. Kaplan-Meier methods estimated OS and 1-year OS from initiation of HMAs to death or end of follow-up. Patients, who underwent allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT) were censored at time of HCT. Survival analysis was stratified according to the MRC/LRF risk tool categories of good, standard and poor risk. Covariates for the MRC/LRF score include age, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG-PS), white blood cell count (WBC) at azacitidine onset, AML type (de novo or secondary) and cytogenetic risk category according to MRC (favorable, intermediate, adverse). Missing data were imputed using the Multivariate Imputation by Chained Equation approach. There were 10 imputed data sets generated from a model with 68 variables using random forest imputation with 500 trees for missing continuous and unordered categorical data, and polytomous logistic regression for missing ordered categorical data. These methods restricted the imputed data to take plausible values found within the original data.
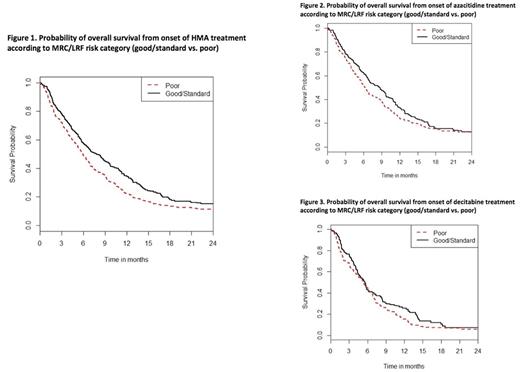
Results: Of 655 patients, 365 patients (56%) had relapsed and 290 (44%) had refractory AML. Median age at start of HMA therapy was 65 years (Range [R], 16-92) and median ECOG PS was 1 with 1.5% of patients having an ECOG PS >2. Median WBC at HMA therapy was 3.2x109/L (R, 0.1-110.5x109/L) and 22.4%, 4.4% and 0.2% of patients had a WBC of > 10x109/L, > 50x109/L and > 100x109/L, respectively. While 458 patients (70.5%) had de novo AML, 192 patients had secondary AML (29.5%). Only 1.8% of patients demonstrated a good risk karyotype based on MRC cytogenetic risk whereas 58.2% and 40% of patients had an intermediate or poor risk karyotype. Applying the MRC/LRF score, 20.9% of patients were categorized as good whereas 24.7% and 54.3% of patients were categorized as standard and poor risk respectively. The median OS for the entire group of patients was 6.2 months (95% CI, 6.0-6.4). Median OS for patients treated with either azacitidine or decitabine (Figure 1) was 6.8 months for patients with either good or standard risk and 5.8 months for patients with poor risk based on MRC/LRF (hazard ratio of death for the poor risk group compared to the good/standard risk group was 1.3, p = 0.090). The1-year OS probability was 29.2% (95% CI 17.8 - 41.2%) vs. 19.6% (95% CI 9.6 - 32.0%) for good/standard risk and poor risk patients, respectively (p = 0.13). For the subgroup of patients treated with azacitidine, median OS for patients with good/standard versus poor risk was 8.5 months compared to 6.2 months (HR = 1.2, p = 0.23). The 1-year OS probability was 32.7% (95% CI 24.2 - 41.4%) vs. 24.2% (95% CI 18.1 - 30.7%) for Poor vs. Good/Standard, p=0.059). For patients treated with decitabine (Figure 3), difference in OS based on MRC/LRF was less pronounced with good/standard risk compared to poor risk patients with a median OS of 5.6 and 5.3 months, respectively (HR = 1.2, p=0.28) and 1-year OS probability of 25.7% (95%CI 15.9 - 36.7%) vs. 15.4% (95%CI 9.0- 23.3%), respectively (p=0.33).
Conclusions: Our results indicate that the MRC/LRF risk tool might be useful for prognostication of OS benefit azacitidine therapy, especially the 1-year OS probability, in the refractory and relapsed setting. However, the tool was not useful prognostically for decitabine use in this setting.
Montesinos: Celgene Corporation: Honoraria, Research Funding. Itzykson: Janssen: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding. Ritchie: Pfizer: Consultancy, Other: Research funding to my institution; NS Pharma: Other: Research funding to my institution; Astellas Pharma: Other: Research funding to my institution; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Other: Research funding to my institution; Novartis: Consultancy, Other: Research funding to my institution, and travel, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Other: Travel, Speakers Bureau. Sekeres: Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Podoltsev: Alexion: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; Ariad: Consultancy; CTI biopharma/Baxalta: Consultancy. Brunner: Celgene: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding. Komrokji: Novartis: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Honoraria. Santini: Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Otsuka: Consultancy; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Roboz: Cellectis: Research Funding; AbbVie, Agios, Amgen, Amphivena, Array Biopharma Inc., Astex, AstraZeneca, Celator, Celgene, Clovis Oncology, CTI BioPharma, Genoptix, Immune Pharmaceuticals, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Juno, MedImmune, MEI Pharma, Novartis, Onconova, Pfizer, Roche Pharmace: Consultancy. Fenaux: Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Astex: Honoraria, Research Funding; Astex: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding. Fathi: Amgen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Juno: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Research Funding; Agios: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Medimmune: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria. Germing: Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria. Zeidan: Takeda: Speakers Bureau; Otsuka: Consultancy; AbbVie, Otsuka, Pfizer, Gilead, Celgene, Ariad, Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal